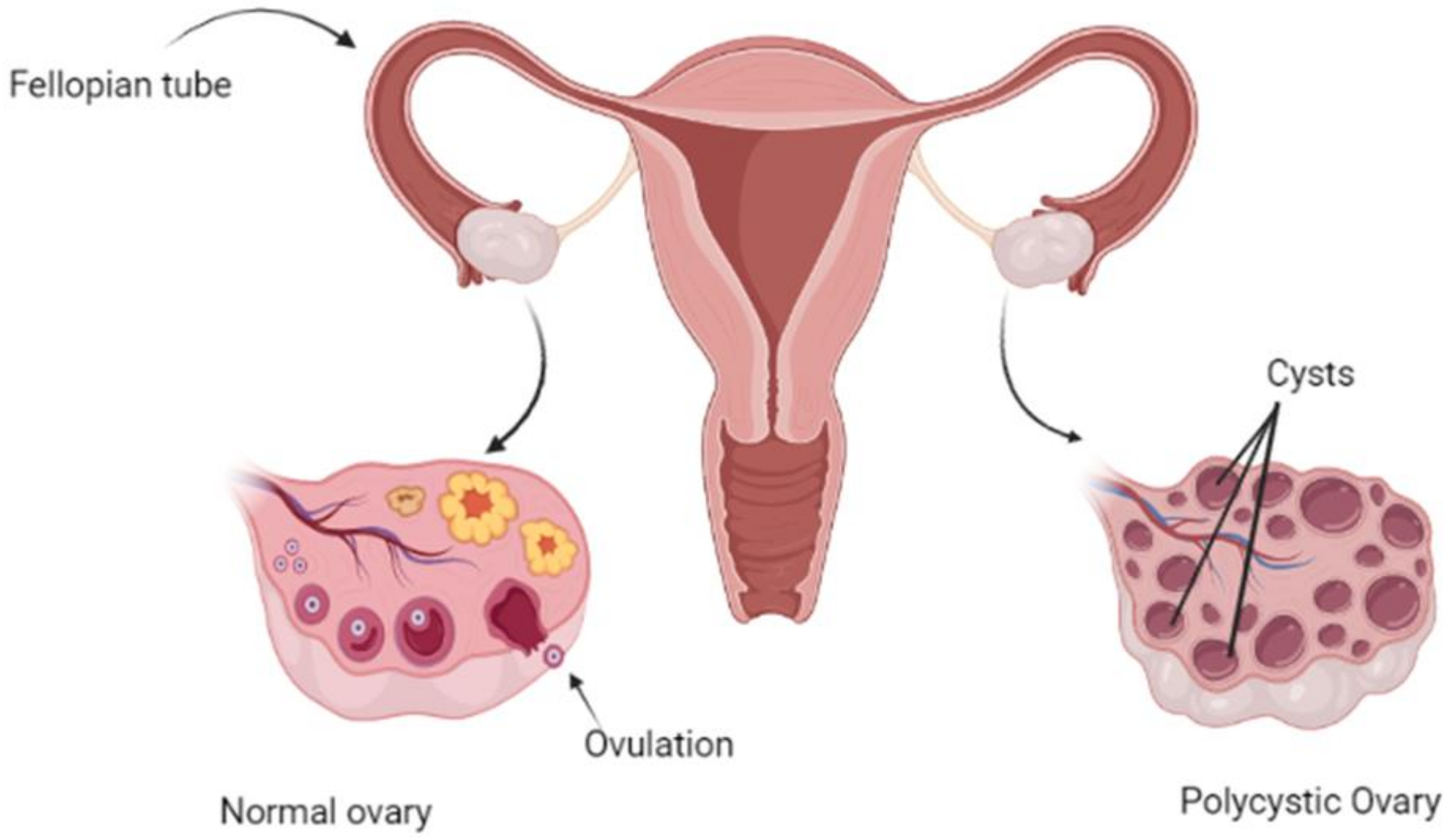
1. Irregular Periods
One of the most common symptoms of PCOS is irregular menstrual periods. Women with PCOS may have fewer than eight menstrual cycles in a year, or may experience long periods that are irregular or absent. This can be caused by the hormonal imbalances associated with PCOS, which can disrupt the normal ovulation process.
Irregular periods can have a significant impact on a woman’s fertility, as irregular or absent periods can make it difficult to predict ovulation and conceive. It can also lead to abnormal uterine bleeding and an increased risk of endometrial cancer if left untreated.
2. Excessive Hair Growth
Another common symptom of PCOS is hirsutism, which is characterized by excessive hair growth on the face, chest, back, and other areas of the body. This is caused by elevated levels of androgens, or male hormones, in women with PCOS. The excess androgens can lead to the growth of coarse, dark hair in areas where women typically don’t have hair.
Excessive hair growth can be embarrassing and affect a woman’s self-esteem. It can also be difficult to manage, as traditional hair removal methods may not be effective. Fortunately, there are treatment options available to help manage hirsutism and reduce the growth of excess hair.
3. Acne
Acne is another common symptom of PCOS, which is also caused by the excess androgens in the body. Women with PCOS may experience persistent acne that is difficult to manage with over-the-counter treatments. The acne may appear on the face, back, chest, and other areas of the body.
Acne can be a source of embarrassment and distress for women with PCOS, affecting their self-esteem and mental well-being. It’s important to seek treatment for acne associated with PCOS to manage the symptoms and improve overall quality of life.
4. Weight Gain
Many women with PCOS experience weight gain, particularly around the abdomen. This is often due to insulin resistance, which is common in women with PCOS. Insulin resistance can cause the body to produce more insulin to regulate blood sugar levels, leading to weight gain and difficulty losing weight.
Weight gain can exacerbate other symptoms of PCOS, such as irregular periods and acne. It can also increase the risk of developing other health conditions, such as type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and heart disease. Managing weight through diet and exercise is an important part of PCOS treatment.
5. Thinning Hair
Thinning hair, or male-pattern baldness, is another symptom of PCOS. This is also caused by the excess androgens in the body, which can disrupt the hair growth cycle and lead to hair loss. Women with PCOS may notice a widening part or thinning of the hair on their scalp.
Thinning hair can be distressing for women with PCOS, as it can affect their self-esteem and confidence. There are treatments available to help manage hair loss associated with PCOS, such as topical solutions and medications. It’s important to address this symptom early to prevent further hair loss.
6. Darkening of the Skin
Some women with PCOS may experience darkening of the skin, particularly in areas such as the neck, groin, and under the breasts. This is known as acanthosis nigricans, and is often a result of insulin resistance. It can appear as dark, velvety patches of skin that may be thicker than normal.
Darkening of the skin can be bothersome for women with PCOS, as it is often a visible sign of the condition. Managing insulin resistance through lifestyle changes and medication can help reduce the appearance of acanthosis nigricans and improve overall skin health.
7. Headaches
Women with PCOS may experience frequent headaches, including migraines. The hormonal imbalances associated with PCOS can lead to changes in estrogen and progesterone levels, which can trigger headaches in some women. The severity and frequency of headaches can vary from woman to woman.
Headaches can be debilitating for women with PCOS, affecting their ability to work, socialize, and perform daily tasks. Managing headaches with medication and lifestyle changes is important to improve quality of life for women with PCOS.
8. Mood Changes
Many women with PCOS experience mood changes, including depression, anxiety, and mood swings. The hormonal imbalances associated with PCOS can disrupt the brain’s chemical messengers, leading to changes in mood and emotional well-being. This can have a significant impact on a woman’s mental health.
Mood changes can affect a woman’s relationships, work, and overall quality of life. It’s important for women with PCOS to seek support and treatment for mood changes, including therapy and medication, to improve their mental health.
9. Sleep Problems
Sleep problems, such as insomnia and sleep apnea, are common in women with PCOS. The hormonal imbalances associated with PCOS can disrupt the body’s natural sleep-wake cycle, leading to difficulty falling asleep and staying asleep. Sleep problems can also be exacerbated by other symptoms of PCOS, such as weight gain and mood changes.
Sleep problems can have a significant impact on a woman’s overall health and well-being. It’s important to address sleep problems early and seek treatment, such as lifestyle changes and sleep apnea therapy, to improve sleep quality for women with PCOS.
10. Fertility Issues
Many women with PCOS experience difficulty getting pregnant, due to irregular ovulation and hormonal imbalances. PCOS is a leading cause of female infertility, affecting a woman’s ability to conceive and carry a pregnancy to term. Women with PCOS may also experience recurrent miscarriages.
Fertility issues can be distressing for women with PCOS, particularly for those who are trying to conceive. Fortunately, there are treatments available to help manage fertility issues associated with PCOS, such as ovulation induction and assisted reproductive technologies.

















