Rosai-Dorfman disease, also known as sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy, is a rare non-cancerous disorder that primarily affects the lymph nodes. This condition is characterized by the overproduction and accumulation of a type of white blood cell called histiocytes, leading to the formation of benign tumors or masses in the lymph nodes and other parts of the body. While the exact cause of Rosai-Dorfman disease is not fully understood, it is believed to be related to an abnormal immune response.
Individuals with Rosai-Dorfman disease may experience a wide range of symptoms, which can vary in severity and may differ from person to person. Understanding the common symptoms associated with this condition is essential for early detection and timely intervention. In this article, we will explore the key symptoms of Rosai-Dorfman disease and how they manifest in affected individuals.
Enlarged Lymph Nodes
One of the hallmark symptoms of Rosai-Dorfman disease is the presence of enlarged lymph nodes, also known as lymphadenopathy. These swollen lymph nodes are typically painless and may be located in the neck, underarms, groin, or other areas of the body. In some cases, the lymph nodes may become so enlarged that they are visible or palpable as lumps under the skin. This can cause discomfort or limited mobility in the affected area, and may prompt individuals to seek medical attention.
Enlarged lymph nodes can also lead to compression of nearby structures, such as blood vessels or nerves, which may result in additional symptoms such as pain, numbness, or tingling in the affected area. It is important to note that while lymph node enlargement is a common feature of Rosai-Dorfman disease, it may also be caused by other conditions, so a thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional is necessary to determine the underlying cause.
Fever and Night Sweats
Many individuals with Rosai-Dorfman disease experience fever and night sweats as a result of the body’s immune response to the overproduction of histiocytes. The presence of fever, often accompanied by chills, may be intermittent or persistent, and can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Night sweats, which may result in drenching of the bedclothes, can disrupt sleep and lead to feelings of fatigue and malaise during the day.
It is important for individuals experiencing fever and night sweats to seek medical attention to rule out other possible causes, such as infection or inflammation. A thorough evaluation, including laboratory tests and imaging studies, may be necessary to establish a diagnosis and determine the most appropriate course of treatment for managing these symptoms.
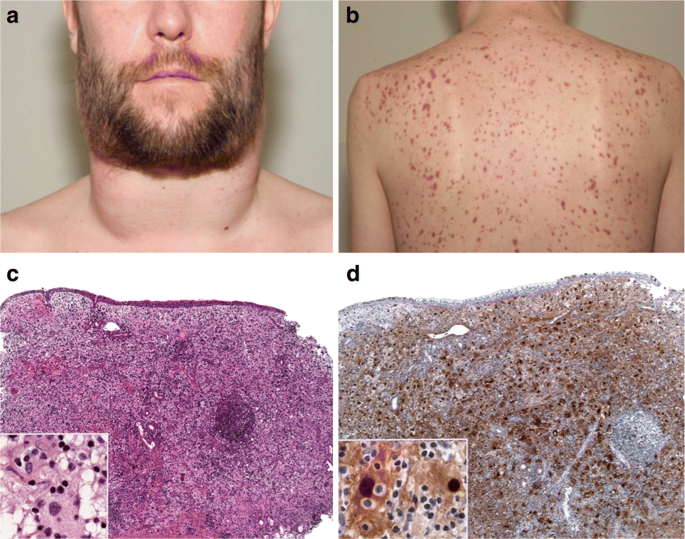
Skin Lesions
In some cases, Rosai-Dorfman disease can manifest with skin lesions or nodules that are visible on the surface of the skin. These lesions may appear as red or purplish bumps, typically located on the face, scalp, or other areas of the body. The presence of skin lesions may be distressing for affected individuals, and can also impact their self-esteem and overall well-being.
Skin lesions associated with Rosai-Dorfman disease may be accompanied by itching, tenderness, or other discomfort. It is important for individuals with these symptoms to seek dermatological evaluation to determine the underlying cause of the skin lesions and develop an appropriate treatment plan. While skin lesions are less common in Rosai-Dorfman disease compared to other symptoms, they are an important clinical feature that should not be overlooked.
Visual or Auditory Impairment
In rare cases, individuals with Rosai-Dorfman disease may experience visual or auditory impairment as a result of the mass effect of enlarged lymph nodes or tumors pressing on surrounding structures. This can manifest as blurred vision, double vision, reduced visual acuity, or changes in color perception. Additionally, individuals may experience auditory symptoms such as hearing loss, tinnitus, or vertigo due to compression of the auditory nerve or other structures in the head and neck region.
Visual or auditory impairment can significantly impact an individual’s ability to perform daily activities and may have a profound effect on their quality of life. It is crucial for affected individuals to seek prompt medical evaluation and management of these symptoms to prevent long-term complications and optimize their functional outcomes.
Respiratory Symptoms
In some cases, Rosai-Dorfman disease may affect the respiratory system, leading to symptoms such as cough, shortness of breath, or chest pain. Enlarged lymph nodes or tumors in the chest cavity can compress the airways or surrounding structures, resulting in respiratory compromise. These symptoms may be exacerbated during physical exertion, such as exercise or strenuous activities, and can significantly impact an individual’s ability to perform daily tasks.
Respiratory symptoms associated with Rosai-Dorfman disease should be evaluated by a healthcare professional to rule out other possible causes, such as pulmonary infections or cardiopulmonary conditions. Imaging studies, such as chest X-rays or CT scans, may be necessary to assess the extent of lung involvement and determine the most appropriate treatment approach.
Neurological Symptoms
Neurological symptoms may occur in individuals with Rosai-Dorfman disease, particularly when the central nervous system is affected. These symptoms can vary widely and may include headaches, dizziness, seizures, or focal neurological deficits, depending on the location and extent of the lesions. Individuals may also experience changes in cognition, mood, or behavior, which can significantly impact their daily functioning and overall well-being.
It is important for individuals experiencing neurological symptoms to seek prompt evaluation by a neurologist or other healthcare provider with expertise in neurology. Imaging studies, such as MRI or CT scans, may be necessary to assess the extent of central nervous system involvement and guide the most appropriate treatment approach for managing these symptoms.
Abdominal Symptoms
Some individuals with Rosai-Dorfman disease may experience abdominal symptoms, such as pain, distension, or discomfort, when the disease affects the lymph nodes or other structures in the abdominal cavity. This can result in gastrointestinal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, or changes in bowel habits, which can significantly impact an individual’s nutritional status and overall well-being.
Abdominal symptoms associated with Rosai-Dorfman disease should be evaluated by a gastroenterologist or other healthcare provider with expertise in gastrointestinal disorders. Imaging studies, such as ultrasound or CT scans, may be necessary to assess the extent of abdominal involvement and determine the most appropriate treatment approach for managing these symptoms.
Generalized Weakness
Generalized weakness or fatigue is a common symptom reported by individuals with Rosai-Dorfman disease, which can significantly impact their overall quality of life. This may result from the body’s immune response to the overproduction of histiocytes or from the systemic effects of the disease on various organ systems. Individuals may experience reduced energy levels, reduced stamina, and a decreased ability to perform daily activities.
It is important for individuals experiencing generalized weakness or fatigue to seek medical evaluation to rule out other possible causes, such as anemia, endocrine disorders, or metabolic conditions. A comprehensive assessment by a healthcare provider is necessary to determine the underlying cause and develop an appropriate treatment plan to address these symptoms.
Weight Loss
Unintentional weight loss is a common symptom reported by individuals with Rosai-Dorfman disease, often as a result of decreased appetite, malabsorption, or systemic inflammation. The presence of weight loss may be concerning for affected individuals and can impact their nutritional status and overall well-being. Individuals may also experience changes in body composition, such as muscle wasting or loss of lean body mass.
It is crucial for individuals experiencing unexplained weight loss to seek medical evaluation to rule out other possible causes, such as malignancy, chronic infections, or gastrointestinal disorders. A thorough assessment by a healthcare provider, including laboratory tests and imaging studies, may be necessary to determine the underlying cause of weight loss and develop an appropriate management plan.
Other Systemic Symptoms
In addition to the symptoms mentioned above, individuals with Rosai-Dorfman disease may experience a wide range of other systemic symptoms, such as malaise, night sweats, anorexia, or joint pain. These symptoms can significantly impact an individual’s overall quality of life and may be related to the systemic effects of the disease on various organ systems.
It is important for affected individuals to seek medical evaluation and management of these symptoms to optimize their functional outcomes and overall well-being. A comprehensive approach, involving a multidisciplinary team of healthcare providers, may be necessary to address the diverse and complex manifestations of Rosai-Dorfman disease.
Conclusion
The symptoms of Rosai-Dorfman disease can vary widely and may affect multiple organ systems, resulting in a significant impact on an individual’s overall quality of life. Early recognition and timely intervention are essential for optimizing functional outcomes and preventing long-term complications. Individuals experiencing symptoms associated with Rosai-Dorfman disease should seek prompt evaluation by a healthcare professional with expertise in the diagnosis and management of this rare disorder.

















