Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency (PKD) is a rare genetic disorder that affects the red blood cells, leading to various health issues. It is important to recognize the symptoms of PKD in order to seek proper diagnosis and treatment. In this article, we will discuss the symptoms of PKD and what you need to know about this condition.
What is Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency?
Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency is a rare inherited disorder that affects the red blood cells, which are responsible for carrying oxygen throughout the body. People with PKD have a mutation in the gene that codes for the enzyme pyruvate kinase, which is essential for the red blood cells’ energy production. Without enough pyruvate kinase, the red blood cells cannot function properly, leading to a condition known as hemolytic anemia.
Symptoms of Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency
The symptoms of Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency can vary from mild to severe, and they may appear at any age. Some common symptoms of PKD include:
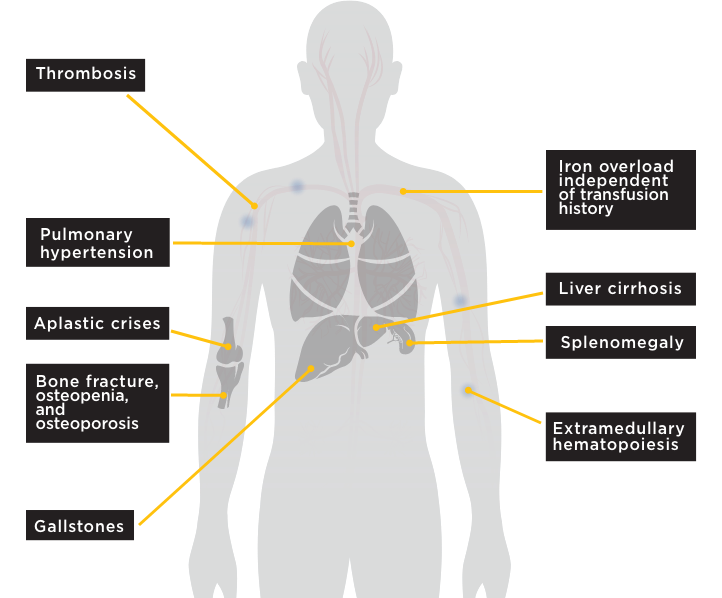
1. Anemia: The most common symptom of PKD is anemia, which can cause fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath. People with PKD may also have pale skin and nail beds due to a lack of oxygen in the blood.
2. Enlarged Spleen (Splenomegaly): Due to the destruction of red blood cells, the spleen becomes enlarged as it works harder to remove the damaged cells from the bloodstream. An enlarged spleen can cause discomfort and fullness in the abdomen.
3. Jaundice: Some people with PKD may develop jaundice, a condition characterized by yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes. Jaundice occurs when the liver cannot process the excessive bilirubin, a pigment produced during the breakdown of red blood cells.
4. Gallstones: People with PKD have an increased risk of developing gallstones, which can cause abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting.
5. Pallor: A lack of red blood cells can lead to a pale appearance in the skin and mucous membranes.
6. Growth and Developmental Delays: Children with PKD may experience growth and developmental delays due to chronic anemia and low energy levels.
Diagnosing Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency
Diagnosing Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency can be challenging due to its rarity and varied symptoms. However, there are several tests that can help in the diagnosis, including:
1. Complete Blood Count (CBC): A CBC can reveal low levels of red blood cells, hemoglobin, and hematocrit, indicating anemia.
2. Blood Smear: A blood smear can show abnormal shapes and sizes of red blood cells, known as poikilocytosis and anisocytosis, which are common in PKD.
3. Hemoglobin Electrophoresis: This test can help rule out other types of anemia and identify the presence of abnormal hemoglobin variants.
4. Genetic Testing: Genetic testing can confirm the presence of mutations in the PKLR gene, which codes for pyruvate kinase.
Treatment and Management of Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency
There is no cure for Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency, but there are several treatment options that can help manage the symptoms and improve quality of life. Some of the treatment and management strategies for PKD include:
1. Blood Transfusions: People with severe anemia may require regular blood transfusions to maintain adequate levels of red blood cells and hemoglobin.
2. Folic Acid Supplements: Folic acid can help increase red blood cell production and reduce the severity of anemia.
3. Splenectomy: In some cases, removing the spleen (splenectomy) can help reduce the destruction of red blood cells and improve anemia.
4. Chelation Therapy: Chelation therapy may be needed to remove excess iron from the body, which can accumulate from regular blood transfusions.
5. Avoiding Triggers: People with PKD should avoid certain triggers that can worsen anemia, such as infections, certain medications, and exposure to toxins.
What You Need to Know
If you or your child experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, it is important to seek medical attention for a proper evaluation and diagnosis. Early diagnosis and management of PKD can help prevent complications and improve quality of life.
Additionally, it is important to seek genetic counseling if you have a family history of Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency. Genetic counseling can help assess your risk of passing on the genetic mutation to your children and guide family planning decisions.
In conclusion, Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency is a rare genetic disorder that can cause a range of symptoms, including anemia, enlarged spleen, jaundice, and growth delays. If you suspect that you or your child may have PKD, seek medical attention for a thorough evaluation and diagnosis. Early diagnosis and management are crucial for improving the quality of life for individuals with Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency. Additionally, consider genetic counseling if you have a family history of PKD to assess your risk and make informed decisions about family planning.

















